3 changed files with 561 additions and 1 deletions
@ -0,0 +1,560 @@ |
|||||
|
# Javase回顾 |
||||
|
## 1.环境 |
||||
|
jdk8及之前:jdk+jre |
||||
|
jdk:java development kit |
||||
|
jre: java runtime environment |
||||
|
jdk8以后:只有jdk |
||||
|
环境变量配置只需要配置JAVAHOME和path里面指向JAVAHOME的bin |
||||
|
## 2.开发工具 |
||||
|
idea(目前最流行) |
||||
|
eclipse(已经不常用) |
||||
|
## 3.基础语法 |
||||
|
### 3.1 java语言特点 |
||||
|
简单,严谨,易读 |
||||
|
编译+解释 |
||||
|
### 3.2 8种基本数据类型 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|数据类型 | 精度 | 范围| |
||||
|
|--|--|--| |
||||
|
| byte | 1 |-2^7^ ~ 2^7^-1(-128~127) |
||||
|
| short | 2|-2^15^ ~ 2^15^-1(-32768 ~ 32767) |
||||
|
| int | 4|-2^31^ ~ 2^31^-1(约21亿多) |
||||
|
|long| 8 |-2^63^~ 2^63^-1(-9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807) |
||||
|
| float | 4 |约±3.4e38(± 3.4 × 10^38^ ) |
||||
|
| double | 8 | 约±1.7e308(± 1.7 × 10^308^ ) |
||||
|
| char | 2 |0 ~ 65535(Unicode) |
||||
|
| boolean | 1(不一定,不同虚拟机不一样 ) | |
||||
|
### 3.3 运算符 |
||||
|
> 算数运算符 :+ - * / % 双目运算符 |
||||
|
> 比较运算符 : > , <, >= , <=, == , != 计算结果是boolean值 |
||||
|
> 逻辑运算符:&& , ||, ! 运算结果是boolean值,存在短路运算 |
||||
|
> 赋值运算符: = ,+=, -=, *= , /= |
||||
|
> 条件运算符 a?b:c 唯一的三目运算符 |
||||
|
> 位运算符:基本用不到 |
||||
|
> 其他运算符:instanceof (例:a instanceof b ) |
||||
|
> 表达式(有值) |
||||
|
> ### 3.4语句 |
||||
|
> java代码执行的基本单位 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
>流程控制语句: |
||||
|
>1.顺序结构: |
||||
|
>2.分支结构: |
||||
|
>3.循环结构: |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.5 数组 |
||||
|
>int[] a = new int[](1,2,3} |
||||
|
>获取数组长度。.length属性,只读。 |
||||
|
>如果访问数组元素。索引(下标),整数,包括0,不能是负数,不能是小数,不能超 |
||||
|
>出边界。 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
public class Test1 { |
||||
|
public static void main(String[] args) { |
||||
|
int[] a = new int[5]; |
||||
|
int[] b = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; |
||||
|
int[] c = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; |
||||
|
System.out.println(c.length); |
||||
|
a[0] = 1; |
||||
|
a[1] = 2; |
||||
|
a[40] = 4; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
import java.util.Arrays; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
public class Test2 { |
||||
|
public static void main(String[] args) { |
||||
|
int[] arr = new int[20]; |
||||
|
//存入随机数 |
||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { |
||||
|
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 100); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
//输出随机数数组 |
||||
|
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); |
||||
|
|
||||
|
boolean found = false; |
||||
|
//判断生成的随机数数组中包不包含50并给出下标 |
||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { |
||||
|
if (arr[i] == 50) { |
||||
|
found = true; |
||||
|
System.out.println(i); |
||||
|
break; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
if (!found) { |
||||
|
System.out.println("无此值"); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
数组应用: |
||||
|
排序:冒泡,选择,快排 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
import java.util.Arrays; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
public class Test3 { |
||||
|
public static void main(String[] args) { |
||||
|
int[] arr = {44, 64, 35, 66, 10, 67, 86, 32, 2, 44}; |
||||
|
quickSort2(arr);//调用函数 |
||||
|
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
//冒泡 |
||||
|
static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) { |
||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { |
||||
|
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) { |
||||
|
if (arr[j] < arr[j + 1]) { |
||||
|
int temp = arr[j]; |
||||
|
arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; |
||||
|
arr[j + 1] = temp; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
static void bubbleSort2(int[] arr) { |
||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { |
||||
|
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) { |
||||
|
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { |
||||
|
int temp = arr[j]; |
||||
|
arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; |
||||
|
arr[j + 1] = temp; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
//选择 |
||||
|
static void selectSort(int[] arr) { |
||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { |
||||
|
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) { |
||||
|
if (arr[j] < arr[i]) { |
||||
|
int temp = arr[j]; |
||||
|
arr[j] = arr[i]; |
||||
|
arr[i] = temp; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
static void selectSort2(int[] arr) { |
||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { |
||||
|
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) { |
||||
|
if (arr[j] < arr[i]) { |
||||
|
int temp = arr[i]; |
||||
|
arr[i] = arr[j]; |
||||
|
arr[j] = temp; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
//快排 |
||||
|
static void quickSort(int[] arr) { |
||||
|
quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
static void quickSort2(int[] arr) { |
||||
|
quickSort2(arr, 0, arr.length - 1); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
//快排实现 |
||||
|
static void quickSort(int[] arr, int low, int high) { |
||||
|
if (low >= high) { |
||||
|
return; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
int pivot = arr[low];//基准值 |
||||
|
int left = low;//左指针 |
||||
|
int right = high;//右指针 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
while (left < right) { |
||||
|
//右指针不断左移 |
||||
|
while (left < right && arr[right] >= pivot) { |
||||
|
right--; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
//左指针不断右移 |
||||
|
while (left < right && arr[left] <= pivot) { |
||||
|
left++; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
if (left < right) { |
||||
|
int temp = arr[left]; |
||||
|
arr[left] = arr[right]; |
||||
|
arr[right] = temp; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
//二者相遇 |
||||
|
if (left != low) { |
||||
|
arr[low] = arr[left]; |
||||
|
arr[left] = pivot; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
//递归 |
||||
|
quickSort(arr, low, left - 1);//对左区递归 |
||||
|
quickSort(arr, left + 1, high);//对右区递归 |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
static void quickSort2(int[] arr, int low, int high) { |
||||
|
if (low > high) { |
||||
|
return; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
int target = arr[low]; |
||||
|
int left = low; |
||||
|
int right = high; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
while (left < right) { |
||||
|
while (left < right && arr[right] >= arr[low]) { |
||||
|
right--; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
while (left<right &&arr[left]<=arr[low]){ |
||||
|
left++; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
if(left<right){ |
||||
|
int temp = arr[left]; |
||||
|
arr[left]=arr[right]; |
||||
|
arr[right]=temp; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
} |
||||
|
//left和right相遇 |
||||
|
if(left!=low){ |
||||
|
arr[low]=arr[left]; |
||||
|
arr[left]=target; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
quickSort2(arr,low,left-1); |
||||
|
quickSort2(arr,left+1,high); |
||||
|
|
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
查找:二分查找 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
public class Test4 { |
||||
|
public static void main(String[] args) { |
||||
|
int[] arr = {2, 10, 32, 35, 44, 44, 64, 66, 67, 86}; |
||||
|
int idx = find2(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, 67); |
||||
|
System.out.println(idx); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
static int find(int[] arr, int low, int high, int target) { |
||||
|
if (low >= high) { |
||||
|
return -1; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
int mid = (low + high) / 2; |
||||
|
if (target == arr[mid]) { |
||||
|
return mid; |
||||
|
} else if (target < arr[mid]) { |
||||
|
return find(arr, low, mid - 1, target); |
||||
|
} else { |
||||
|
return find(arr, mid + 1, high, target); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
static int find2(int[] arr, int low, int high, int target) { |
||||
|
if (low >= high) { |
||||
|
return -1; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
int mid = (low + high) / 2; |
||||
|
if (target == arr[mid]) { |
||||
|
return mid; |
||||
|
} else if (target < arr[mid]) { |
||||
|
return find2(arr, low, mid - 1, target); |
||||
|
|
||||
|
} else { |
||||
|
return find2(arr, mid + 1, high, target); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.6 函数(方法) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.7 面向对象 |
||||
|
类:类型,将很多实例抽取共性,总结归纳 |
||||
|
对象:独一无二的实例,在java中,对象通过类创建 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
创建对象:new 构造方法() |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.8封装 |
||||
|
将成员属性和成员方法包含到一个类中,选择性的对外开放成员。 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
成员访问修饰符:对外开放程度 |
||||
|
public:公开,公有的,任何位置都可访问。 |
||||
|
protected:受保护的,包内及后代可以访问。 |
||||
|
<空>:包内访问。 |
||||
|
private:当前类内部访问。 |
||||
|
### 3.9 继承 |
||||
|
单继承,默认继承自object,顶级根类 |
||||
|
1.非私有成员可以被继承 |
||||
|
2.构造函数不能被继承 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
protect: |
||||
|
super:父对象 |
||||
|
this:当前对象 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
package com.situ.chapter1; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
public class Person { |
||||
|
public int age;//年龄 |
||||
|
private String name;//姓名 |
||||
|
//无参构造方法 |
||||
|
public Person() { |
||||
|
|
||||
|
} |
||||
|
//有参构造 |
||||
|
public Person(String name) { |
||||
|
this.name = name; |
||||
|
System.out.println("创建Person对象"); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
//行为 |
||||
|
protected void sayHello() { |
||||
|
System.out.println("父亲sayHello"); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
void wang() { |
||||
|
System.out.println("aaa"); |
||||
|
sayHello(); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
package com.situ.chapter1; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
public class Teacher extends Person { |
||||
|
|
||||
|
public Teacher() { |
||||
|
super(); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
@Override |
||||
|
protected void sayHello() { |
||||
|
System.out.println("儿子sayHello"); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
public void sayBye() { |
||||
|
this.sayHello(); |
||||
|
super.sayHello(); |
||||
|
|
||||
|
//System.out.println(super.name); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
package com.situ.chapter1; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
public class Test1 { |
||||
|
public static void main(String[] args) { |
||||
|
Person person = new Person(); |
||||
|
person.sayHello(); |
||||
|
person.wang(); |
||||
|
System.out.println("---------------"); |
||||
|
Teacher teacher = new Teacher(); |
||||
|
teacher.sayHello(); |
||||
|
teacher.sayBye(); |
||||
|
|
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
访问构造函数: |
||||
|
this(xxx):调用当前类的构造函数 |
||||
|
super(xxx):调用父类的构造函数 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
构造函数:对对象的成员属性进行初始化 |
||||
|
1.与类同名 |
||||
|
2.无返回值 |
||||
|
3.如果一个类没有显式定义构造函数,会自动创建一个公有的无参的构造函数,如果显式指定了构造函数,就不会再自动创建无参构造函数 |
||||
|
4.构造函数是类成员,可以指定修饰符 |
||||
|
5.创建对象时,使用new<构造函数>(xxx) |
||||
|
6.创建子类对象时,必须先调用父类的构造函数 |
||||
|
7.一个构造函数的第一句代码必须是this(xxx)或者super(xxx),有且只有一次调用 |
||||
|
8.如果没有显式调用this(xxx)或super(xxx),默认调用super() |
||||
|
### 3.10 多态(非常重要) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
在程序运行期间,同一行为,表现出多种形态 |
||||
|
1.继承或接口 |
||||
|
2。重写 |
||||
|
3.使用一个父类型(祖先类型)的引用指向一个子类(后代类)的实例 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
package com.situ.chapter2; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
public class Animal { |
||||
|
public void run() { |
||||
|
System.out.println("动物在跑"); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
package com.situ.chapter2; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
public class Cat extends Animal { |
||||
|
private static String name; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
@Override |
||||
|
public void run() { |
||||
|
System.out.println("猫在跑"); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
package com.situ.chapter2; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
public class Fish extends Animal { |
||||
|
@Override |
||||
|
public void run() { |
||||
|
System.out.println("鱼在跑"); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
package com.situ.chapter2; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
public class Test1 { |
||||
|
static int a = 10; |
||||
|
public static void main(String[] args) { |
||||
|
Animal animal = new Cat(); |
||||
|
run(animal); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
static void run(Animal animal) { |
||||
|
animal.run(); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
### 3.11 static和final |
||||
|
static成员即类成员,属于类的,不属于某个对象,通过类名称直接访问 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
final:表示最终的,不变的 |
||||
|
1.修饰类,表示类不能被继承 |
||||
|
2.修饰方法:表示方法不可被重写 |
||||
|
3.修饰变量:表示变量为不可变的变量(常量) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.12 抽象类和接口 |
||||
|
抽象方法:只有方法定义,没有实现的方法,叫抽象方法 |
||||
|
抽象类:使用abstract关键字 |
||||
|
1.使用abstract关键字 |
||||
|
2.不能创建实例(对象) |
||||
|
3.除此之外,和普通类没有区别。 |
||||
|
4.可以有构造函数。 |
||||
|
5.抽象类中允许有抽象方法(也可以没有),普通类中一定没有抽象方法。 |
||||
|
6.一个类中只要有抽象方法,则必须是抽象类 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
接口: |
||||
|
1.接口不是类。 |
||||
|
2.接口中只能有抽象方法(),jdk1.8之后新增:静态方法(static)和默认方法(default) |
||||
|
3.接口中的方法默认是public abstract修饰,不写也行 |
||||
|
4.接口中的静态方法和类中的静态方法类似 |
||||
|
可直接接口名调用 |
||||
|
5.接口中的默认方法可被继承到实现类中,在默认方法中可以使用this关键字,由实现类来调用 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
接口提供一定的规范和约束,不提供实现 |
||||
|
实现类去实现接口 implements实现接口 |
||||
|
实现类必须对接口中的方法提供实现,如果不能,则只能为抽象类 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.13 常用类 |
||||
|
1.Object:所有类的终极父类。没有父类 |
||||
|
hashCode:用于生成对象的唯一(尽量唯一)标识码 |
||||
|
默认返回对象的内存地址。 |
||||
|
equals:用于判定两个对象是否逻辑上相等,逻辑是由程序员决定的,重写。默认比较是否同一个内存地址 |
||||
|
toString:将一个对象以字符串的形式展示 |
||||
|
clone():克隆一个对象 |
||||
|
getClass:获取对象的类型实例(Class) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
2.String:表达式字符串,不可继承。内容不可变 |
||||
|
3.Math:数学相关方法 |
||||
|
4.Date:日期相关。LocalDate,LocalTime,LocalDateTime |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.14 集合相关类: |
||||
|
1.List:ArrayList,LinkedList.列表:有序,可重复。 |
||||
|
2.set:HashSet 集合,无序,不重复 |
||||
|
3.Map:HashMap 映射:存储键-值对,键无序,不重复 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.15 泛型 |
||||
|
<T> 类型变量 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.16异常 |
||||
|
程序出错时的处理方式.挽救或补回措施 |
||||
|
try...catch...finally |
||||
|
caatch可以已有多个分支,第一个分支,捕获某一个类型的异常 |
||||
|
finally分支中的代码一定会执行,无论是否出现异常 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
异常是有类型的 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
异常分两种: |
||||
|
异常分成两种: |
||||
|
1.编译时异常,检查异常 ,checkedException。在编译期就要求处理异常。 |
||||
|
2.运行时异常。RuntimeException。 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.17 IO |
||||
|
Input & Output 流对象完成输入输出的 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
流动的方向分为输入流和输出流 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
流动的单位:字节流和字符流 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
介质类型:文件流,网络流,数组流 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
以Stream结尾的是字节流 |
||||
|
以InputStream结尾的是输入流 |
||||
|
流在使用完之后必须关闭,如果忘记,容易内存泄漏 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
throws:写在方法后面,表示此方法向上抛出异常 |
||||
|
throw:原地抛出(触发,引发)异常 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.18 多线程 |
||||
|
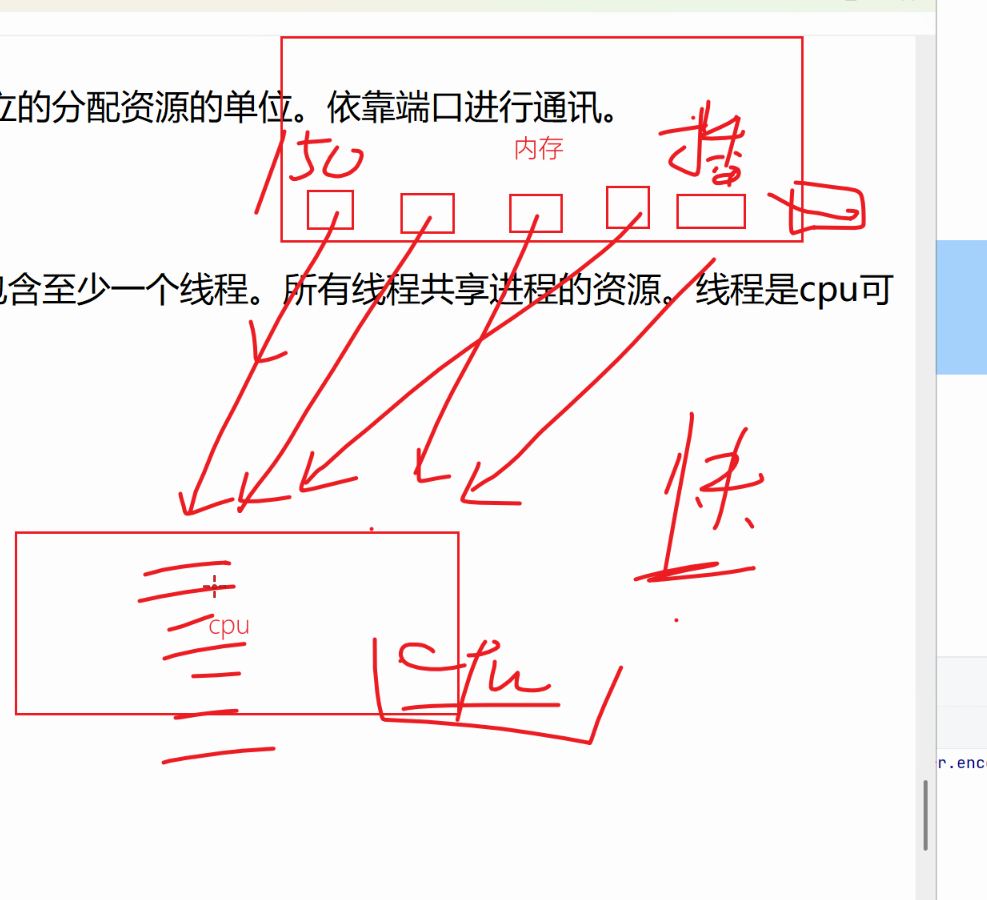
进程:Process,操作系统管理的独立的分配资源的单位,依靠端口进行通信 |
||||
|
一个程序至少有一个进程。 |
||||
|
如:QQ此时6个进程 |
||||
|
 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
线程:Thread。一个进程中可以包含至少一个线程。所有线程共享进程的资源。线程是cpu可调度的最小单位 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
cpu:单核。一个核心。 |
||||
|
多核。真正的并行。 |
||||
|
web开发程序都是并行的,多线程。 |
||||
|
 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.18 反射 |
||||
|
反射:java的灵魂,在程序运行期间,在无法直接使用目标类的情况下,以一种间接的方式,去操作对象。 |
||||
|
Reflect: 镜像。 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
常用类: |
||||
|
Class: 描述其他类,描述类的类 |
||||
|
Field: 描述字段的类。描述成员属性 |
||||
|
Method:描述成员方法的。 |
||||
|
Constructor:描述构造函数的。 |
||||
|
Parameter:描述方法的参数的。 |
||||
|
Annotation:描述注解的。 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
获取Class类型实例三种方式: |
||||
Write
Preview
Loading…
Cancel
Save
Reference in new issue