5 changed files with 314 additions and 0 deletions
-
BIN尹顺宇学习笔记/尹顺宇11.07作业/11.07学习总结.docx
-
314尹顺宇学习笔记/尹顺宇11.07作业/尹顺宇11.07SpringBoot.md
-
BIN尹顺宇学习笔记/尹顺宇11.07作业/尹顺宇11.07SpringBoot.pdf
-
BIN尹顺宇学习笔记/尹顺宇11.07作业/尹顺宇11.07股票学习总结.docx
-
BIN李延霜学习笔记/李延霜前端知识点11.7.pdf
@ -0,0 +1,314 @@ |
|||||
|
## SpringBoot |
||||
|
注:下面的版本号1.0,2.0等等仅代表发展历程演变,不代表该技术真实发布版本号 |
||||
|
### web开发初级阶段: |
||||
|
servlet+jsp web开发的初级阶段。mvc三层架构 m:model v:view c:controller |
||||
|
### web开发推进发展1.0 |
||||
|
之后同一时期出现三种: |
||||
|
SSH |
||||
|
struct 1.0 起初解决mvc 扩展名为.do的网站 |
||||
|
spring 1.0 起初专注于创建对象。单例对象。 |
||||
|
hibernate 1.0 :orm关系映射。将数据库中的结果集转换为Java对象,无需自己写sql。 |
||||
|
### web开发推进发展2.0 |
||||
|
之后发展: |
||||
|
SSH2 |
||||
|
struct 2.0 .action扩展名 |
||||
|
spring 2.0 加入aop功能,面向切面功能 |
||||
|
mybaits:orm 轻量级,需要程序员自己写sql |
||||
|
hibernate 2.0+ |
||||
|
### web开发推进发展3.0 |
||||
|
SSM |
||||
|
需要使用xml进行配置 |
||||
|
springMVC:解决MVC,替代struct2.0 |
||||
|
Spring 3.0+ 增加更多功能,模块化 |
||||
|
mybaits 3.0+ 替代hibernate |
||||
|
|
||||
|
微服务:把一个大项目拆分成小的项目,然后根据需要进行整合。(例如:微信上面的小程序)规模小 |
||||
|
SpringBoot 不是一个框架。一个快速开发脚手架。快速开发,在一定程度上限制了自由性,有固定的目录结构,有约定俗成的配置。 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
> 约定大于配置 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
SpringBoot != SSM |
||||
|
SpringBoot整合SSM |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
### idea配置一个springboot项目: |
||||
|
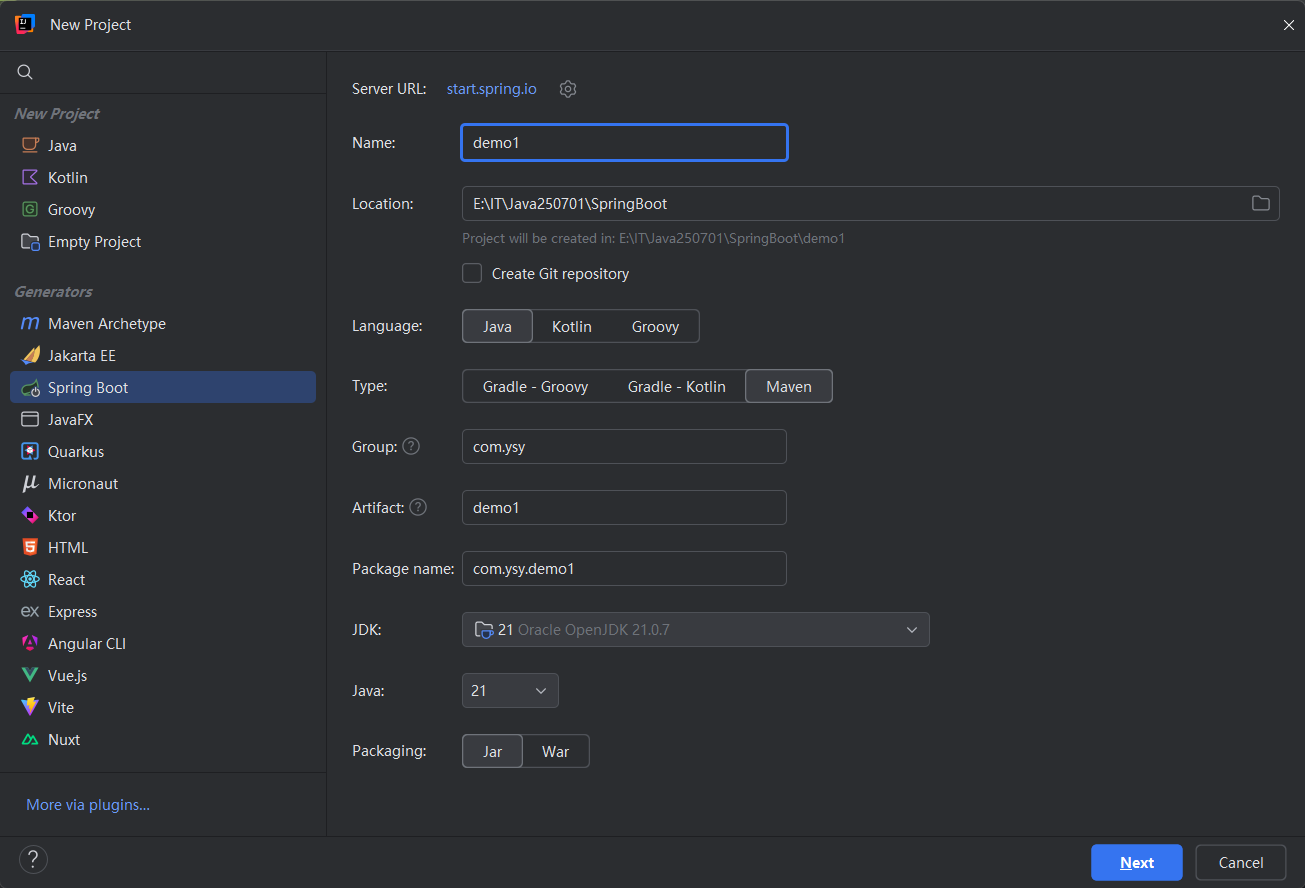 |
||||
|
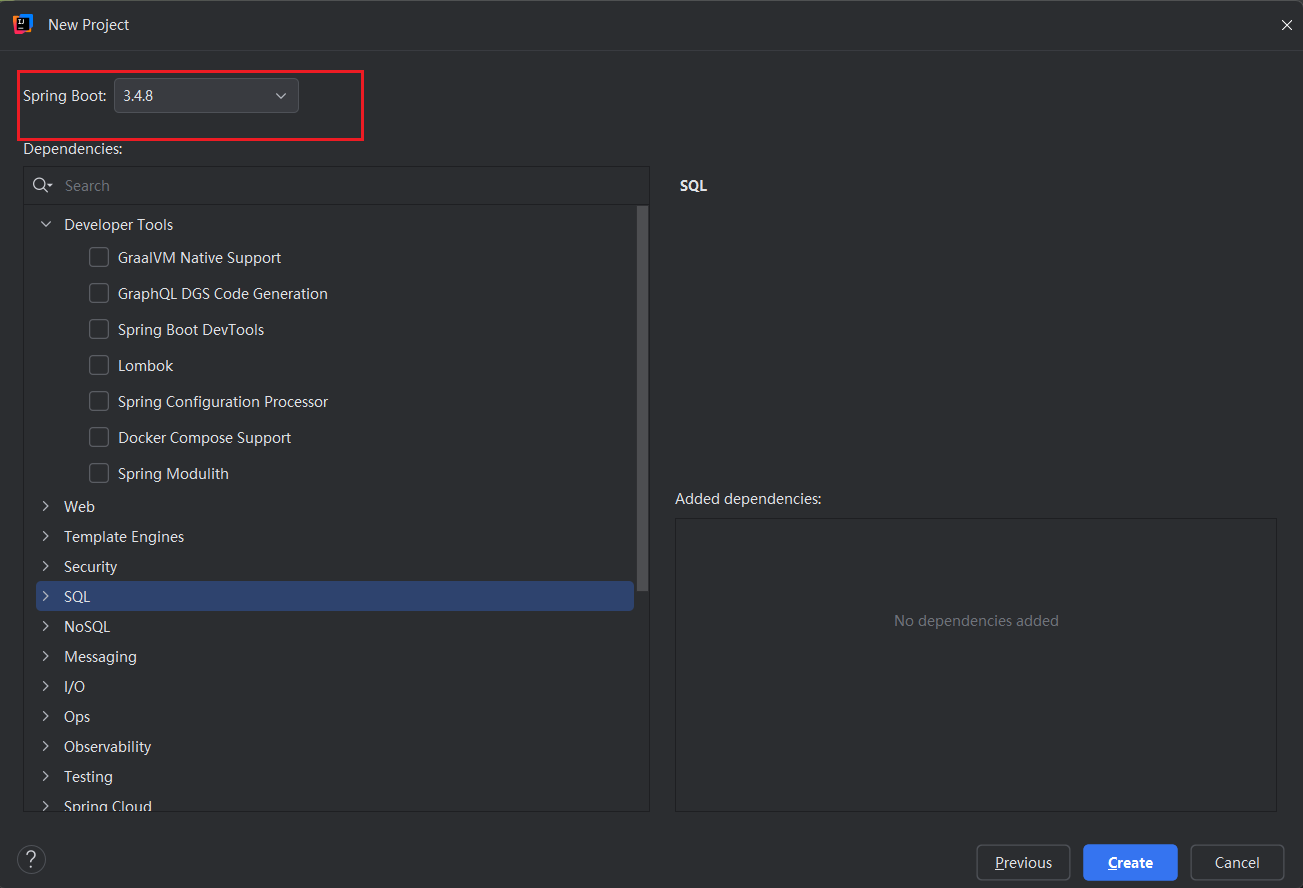 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
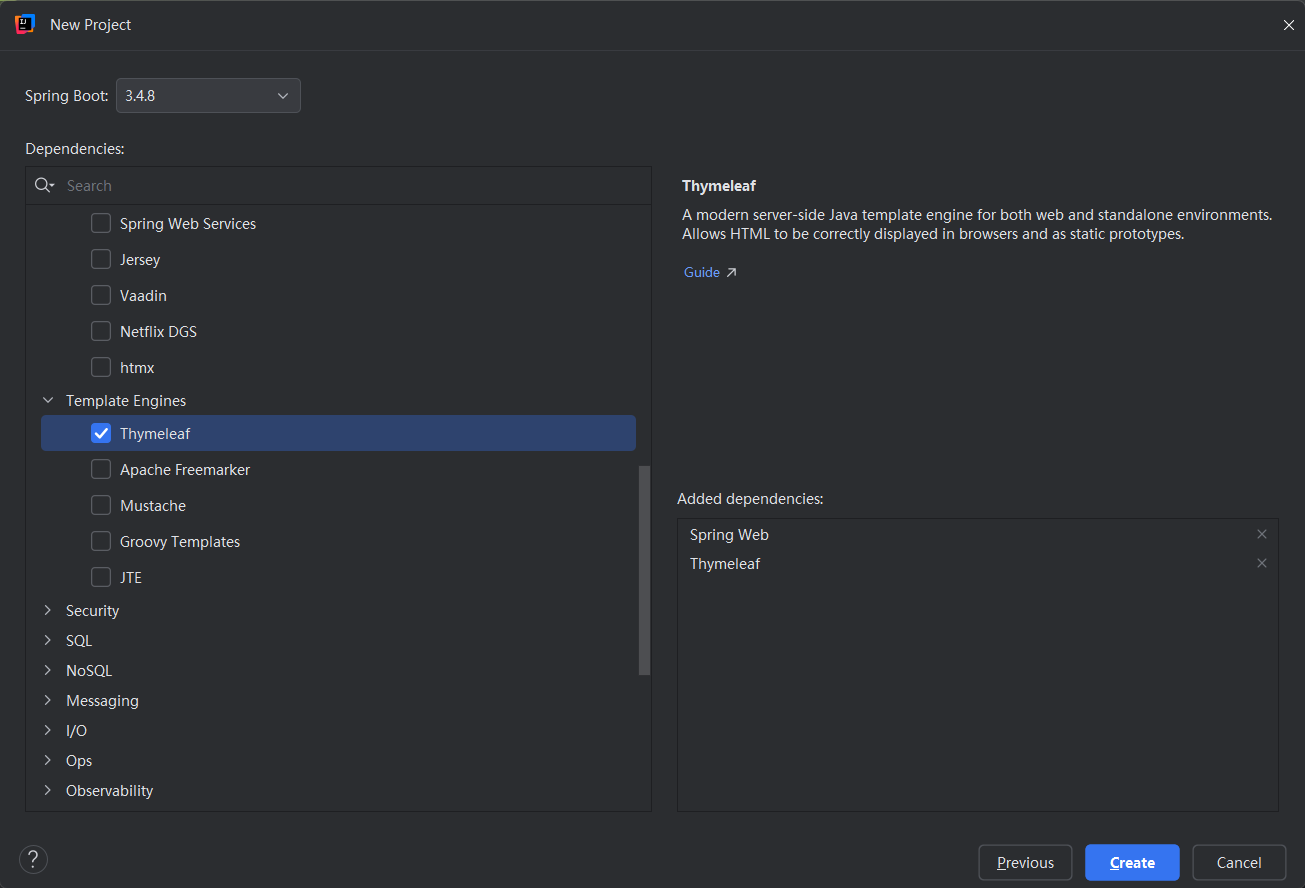 |
||||
|
根包:com.ysy |
||||
|
主启动类 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
以spring- boot-start开头的依赖是启动器,自动配置 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### Spring框架的两项核心功能 |
||||
|
#### 一. 控制反转 |
||||
|
Spring:将创建对象的权限交给spring框架,称之为控制反转 Inverse Of Control 简称ioc |
||||
|
|
||||
|
> IOC概念理解如下图,借鉴自:https://blog.csdn.net/bestone0213/article/details/47424255?fromshare=blogdetail&sharetype=blogdetail&sharerId=47424255&sharerefer=PC&sharesource=ysy1648067239&sharefrom=from_link |
||||
|
>  |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### 二. 依赖注入 |
||||
|
Spring框架自动将容器中的实例,自动赋值给需要的类,DI |
||||
|
Autowired: 依赖注入注解 |
||||
|
##### 2.1依赖注入的三种方式: |
||||
|
###### 2.1.1字段注入 |
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
@Autowired |
||||
|
private StudentService studentService ; |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
###### 2.1.2setter注入 |
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
@Autowired |
||||
|
public void setStudentService(StudentService studentService) { |
||||
|
this.studentService = studentService; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
###### 2.1.3 构造器注入 |
||||
|
构造器注入可以省略Autowired注解 |
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
@Autowired //构造器注入可以省略此行注解 |
||||
|
public StudentController(StudentService studentService){ |
||||
|
this.studentService= studentService; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
#### 2.2 依赖注入相关注解解释: |
||||
|
##### 2.2.1 @Autowired |
||||
|
1.默认按类型匹配 使用频率比较高 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
@Autowired |
||||
|
private StudentService studentService; |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
就会去容器里去找StudentService类型的实例去匹配,此时不加其他注解的前提下,容器里只能有一个该类型的实例,否则注解就不知道该去找哪个实例。 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
**当有多个匹配时** |
||||
|
1.可以使用@Primary注解表示优先 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
> 比如StudentServiceImpl和MyStudentServiceImpl两个类均实现StudentService接口进行实例化,那么,@Primary加在哪个类上,哪个类优先级就高,@Autowired就会优先去找这个类 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
2.按名称匹配 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
> 首先,@Component变成@Component("i1"),也就是括号里加上名字,(@Component注解不加括号写名字时,默认的名字是@Component下类名的首字母小写) |
||||
|
> 然后,cotroller层需要搭配 @Qualifier()注解,加上 @Qualifier(“i1”)。此时, |
||||
|
> @Autowired注解就会找 @Qualifier(“i1”)指定的@Component("i1")所在的类实例化 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
##### 2.2.2@Resource注解: |
||||
|
功能类似于 Spring 的 @Autowired 注解,也是用于依赖注入,默认是按名称进行装配(byName),如果找不到匹配的名称,则按类型装配(byType) |
||||
|
1.默认按名称匹配注入 按name值 |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
@Resource(name = "i1") |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
2.按类型匹配注入:通过type属性 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
@Resource(type = StudentService.class) |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
3.上面两个结合使用: |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
@Resource(type = StudentService.class,name = "i1") |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
##### 2.2.3 @Component注解的变种 |
||||
|
首先回顾@Component注解的作用: |
||||
|
> 当一个类被标记为 @Component 时,Spring 容器会在启动时自动扫描并实例化这个类,并将其注册到 Spring 上下文中 |
||||
|
> @Component 注解可以用于任何类,包括控制器、服务、DAO 等。当一个类被标记为 @Component 时,它就成为了 Spring 上下文中的一个 bean,可以被其他 bean 通过依赖注入的方式使用。 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
该注解的“变种”: |
||||
|
> spring官方认为@Component注解过于中性,不易理解,所以引入了以下几种进行区分 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
@Service 用于标注业务层组件 |
||||
|
@Repository (仓储)用于标注数据访问组件,即DAO组件 |
||||
|
@Controller 用于标注控制层组件 |
||||
|
@RestController 本质上是 @Controller + @ResponseBody,因此无需每个方法都添加 @ResponseBody,简化了开发。除了具有@controller的功能之外,还会实现@ResponseBody ,也就是声明返回值 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
> @Component 和@Service,@Repository (仓储),@Controller |
||||
|
> ,@RestController一样,自动创建唯一实例 ,在目前的 Spring 版本中,这 3 个注释和 @Component 是等效的,但是从注释类的命名上,很容易看出这 3 个注释分别和持久层、业务层和控制层(Web 层)相对应。 |
||||
|
> 虽然目前这3 个注释和 @Component 相比没有什么新意,但 Spring 可能将在以后的版本中为它们添加特殊的功能。 |
||||
|
##### @Component与@Bean的区别和联系 |
||||
|
@Component 作用于类,@Bean作用于方法。 |
||||
|
@Bean 需要在配置类中使用,即类上需要加上@Configuration注解 |
||||
|
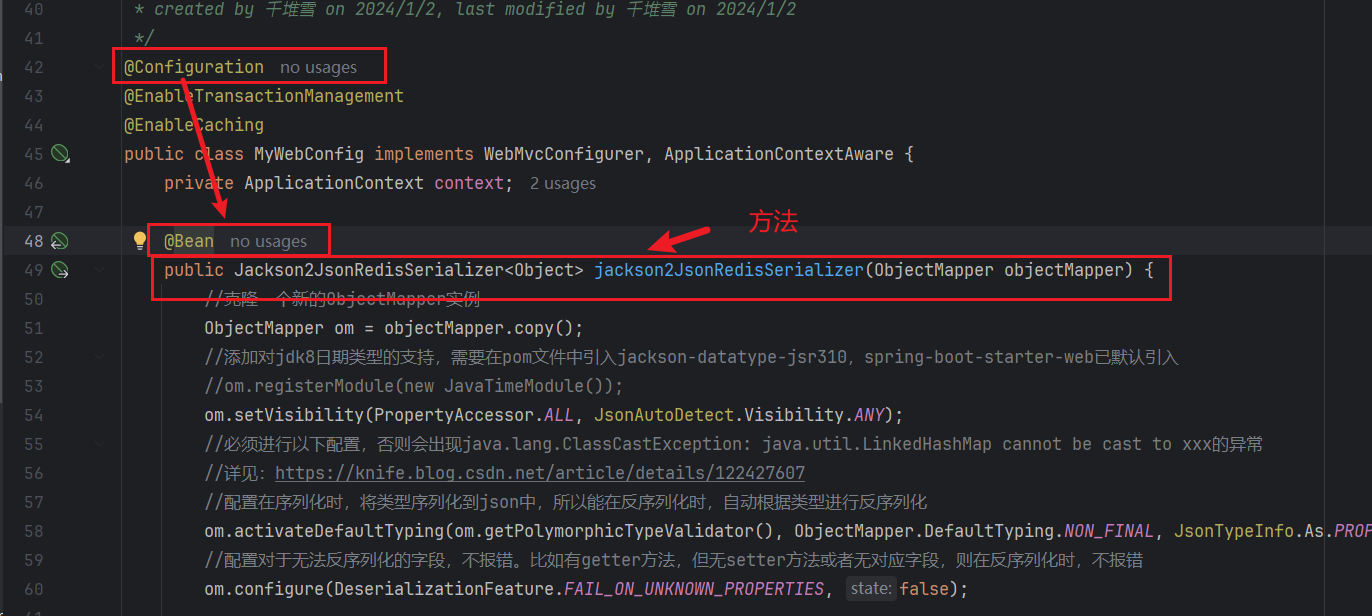 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
相同点:两者的目的是一样的,都是注册bean到Spring容器中。 |
||||
|
两者都可以通过@Autowired装配 |
||||
|
##### 有@Component为何还需要@Bean呢? |
||||
|
如果你想要将第三方库中的组件装配到你的应用中,在这种情况下,是没有办法在它的类上添加@Component注解的,因此就不能使用自动化装配的方案了,但是我们可以使用@Bean,就像上图那种方法。 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### 各种@xxxMapping注解 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
在Controller中,一个方法只有指定@XXXMapping才能接收并处理请求 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
1.@GetMapping:接收get类型的请求 |
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
@GetMapping(value = "/student/list",produces = |
||||
|
"application/json;charset=utf-8") |
||||
|
//produces是指定数据类型 |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
2.@PostMapping接收post类型的请求 |
||||
|
3.@PutMapping接收put类型的请求 |
||||
|
4.@PatchMapping接收patch类型的请求 |
||||
|
5.@DeleteMapping接收delete类型的请求 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
6.@RequestMapping 是一个通用的注解,接收任意类型的请求,但可以指定类型,produces属性指定响应类型,这是最早的注解,后来为了方便使用,根据HTTP方法细分出了上述的专用注解。 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
@RequestMapping(value = "/student/list",method ={ |
||||
|
RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST}) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
> 这些@xxxMapping也可以添加到类上。表示所有方法以类上定义的路径作为公共的前缀。全局统一定义 |
||||
|
> |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### SpringMvc 方法的参数类型 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
> 这里说的SpringMvc 方法一般就是指在controller层里,被各种@xxxMapping注解修饰的方法,比如查询所有学生方法,删除学生信息方法 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
1.可以是HttpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse,HttpSession |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
public String list(Map<String, Object> map, |
||||
|
HttpServletRequest request) { |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
2.可以是基本数据类型,以及包装类,BigDecimal,BigInteger,String,用于接收请求中的参数 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
public String list(Map<String, Object> map,int pages,int limit ,String order) { |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
如果前端url里写的sort=id,但后端就是想用order接收,那么 |
||||
|
搭配@RequestParam ,@PathVariable注解 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
public String list(Map<String, Object> map, |
||||
|
int pages,int limit , |
||||
|
@RequestParam("sort") String order) { |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
> @RequestParam("sort")还可以加默认值,也就是@RequestParam("sort",defaultValue ="name") |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
@GetMapping(value = "/list/{limit}",produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) |
||||
|
public String list(Map<String, Object> map, |
||||
|
int pages, |
||||
|
@PathVariable Integer limit , |
||||
|
@RequestParam("sort") String order) { |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
> url里list/后写15,此时的15会直接赋给带有 @PathVariable注解且名字为limit的变量 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
@GetMapping(value = "/list/{a1}",produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) |
||||
|
public String list(Map<String, Object> map, |
||||
|
int pages, |
||||
|
@PathVariable("a1") Integer limit , |
||||
|
@RequestParam("sort") String order) { |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
> @PathVariable也可以指定名字,如 @PathVariable("a1") |
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
@GetMapping(value ={"/list/{a1}","/list"},produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) |
||||
|
public String list(Map<String, Object> map, |
||||
|
int pages, |
||||
|
@PathVariable("a1") Integer limit , |
||||
|
@RequestParam("sort") String order) { |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
> 如果加上required = false,也就是 @PathVariable("a1",required = |
||||
|
> false)代表url里list/后可以不写{a1} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
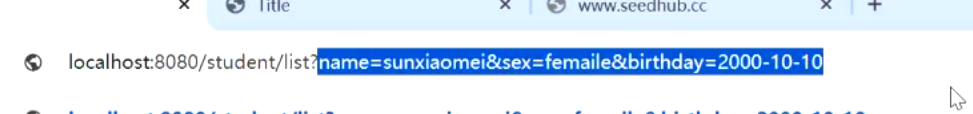
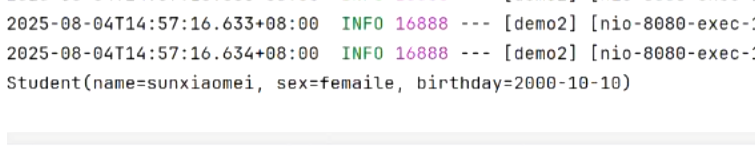
3.JavaBean 普通类将请求参数通过反射,设置到javabean实例中 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
public String list(Map<String, Object> map, |
||||
|
Student student) { |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
 |
||||
|
 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
4.Map,Model,ModelMap:充当请求域,map最常用 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
public String list(Map<String, Object> map, |
||||
|
Model model,ModelMap modelMap ) { |
||||
|
List<Student> students = studentService.findAll(); |
||||
|
map.put("students", students); |
||||
|
model.addAttribute("students",students); |
||||
|
|
||||
|
modelMap.addAttribute("modelMap",students); |
||||
|
modelMap.put("students",students); |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
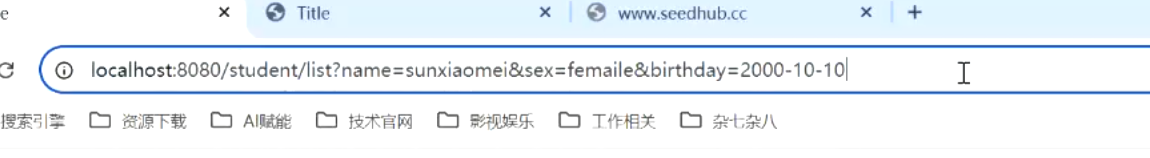
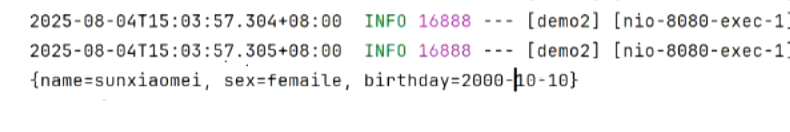
5.加了@RequestParam的map不再作为请求域而是用于存储请求参数 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
public String list(Map<String, Object> map, |
||||
|
@RequestParam Map<String, Object> map1 ) { |
||||
|
System.out.println(map1); |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
 |
||||
|
 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
以上五种参数任意组合 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### SpringMvc 方法的返回值 |
||||
|
1.字符串且响应内容类型为text/html,返回值即模板文件名 |
||||
|
比如: |
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
//请求转发 |
||||
|
return "/student/list"; |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
2.在满足1的基础上,返回"forword:/xxx"表示请求转发 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
return "forward:/student/list"; |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
3.在满足1的基础上,返回“redirect:/xxx”表示重定向 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
return "redirect:/student/list"; |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
4.ModelAndView:既可以指定视图名称,同时可以当请求域使用,前三种本质上也会被包装成ModelAndView |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
@GetMapping("/to_list") |
||||
|
public ModelAndView toList(){ |
||||
|
|
||||
|
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("student/list");//做视图 |
||||
|
mav.addObject("students",studentService.findAll());//做模型 |
||||
|
return mav; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
} |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
5.如果指定了响应内容类型为json,并且添加了@ResponseBody注解,无论返回值什么类型,都会序列化成json字符串 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
//响应json内容 |
||||
|
@GetMapping(value = "/student/list_json",produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE) |
||||
|
@ResponseBody |
||||
|
public ResponseEntity<List<Student>> list(){ |
||||
|
return "student/list" |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
6.返回ResponseEntity类型。仅限于响应json格式,同时封装了业务数据以及状态码 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
```java |
||||
|
//响应json内容 |
||||
|
@GetMapping(value = "/student/list_json",produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE) |
||||
|
@ResponseBody |
||||
|
public ResponseEntity<List<Student>> list(){ |
||||
|
List<Student> students = studentService.findAll(); |
||||
|
return ResponseEntity.status(200).body(students); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
``` |
||||
Write
Preview
Loading…
Cancel
Save
Reference in new issue